New analysis appears to be like on the elements that velocity up and decelerate HTA value determinations for uncommon illness medicines across Europe.
Rare illnesses drugs have all the time confronted challenges in the case of HTA approvals, at the same time as governments convey in additional regulatory insurance policies that make their path by evaluation simpler.
Several elements make it troublesome for HTA our bodies usually to evaluate orphan drugs, together with a scarcity of strong trial information on account of difficulties find sufferers, the absence of randomised managed trials, using surrogate endpoints, and the shortage of energetic drug comparators.
A brand new evaluation from consulting agency CRA has honed in on the completely different challenges confronted in 4 European markets – England, France, Germany and Scotland – and checked out how producers can enhance the probabilities of a profitable appraisal.
The analysis analysed greater than 70 EMA-approved uncommon illness therapies and in contrast reimbursement suggestions from the regulatory our bodies in every nation, to see how HTA choices doubtlessly extended time to reimbursement.
The outcomes present that HTAs for orphan drugs can range broadly across Europe, inflicting inconsistencies in proof necessities and suggestions.
Rates of approval
The research reviewed all 80 European Medicines Agency (EMA) authorised drugs receiving an orphan designation between 1 January 2013 and 31 December 2019, analysing their HTA outcomes and time to reimbursement across France, Germany, England and Scotland.
A comparative evaluation was then performed on the 71 accepted drugs that achieved a negotiated value in no less than one of many 4 markets.
Germany had the very best approval charge of orphan drugs at 98% – nevertheless most of those suggestions (73%) had been awarded a ‘non-quantifiable benefit’ ranking, the automated ranking for an orphan drug, which exhibits the regulator didn’t see any profit in comparison with comparator merchandise (see graph 1). The authors additionally notice that orphan drug trials with increased p values and surrogate endpoints are sometimes accepted for evaluation within the nation.
A extra beneficial consequence from the German regulator took on common 1.four instances longer to realize a closing negotiated value (708 versus 510 days).
Graph 1: Assessment of the HTA consequence in France, Germany, England and Scotland of all orphan drugs that obtained an EMA approval between 2013-2019. N above every bar equals the variety of drugs reviewed by the respective HTA physique. Source: CRA Analysis
France and England had comparable approval charges (92% and 91%, respectively); nevertheless, France reviewed nearly twice the variety of orphan drugs over the interval of study (67 versus 35). Only 19% of the orphan drugs in France had been awarded an Amelioration du Service Médical Rendu (ASMR) ranking of V, which signifies no enchancment in medical profit. Drugs with an ASMR IV-V ranking had been reimbursed in 427 days, in comparison with 585 days for merchandise with ASMR I-III (see Graph 2).
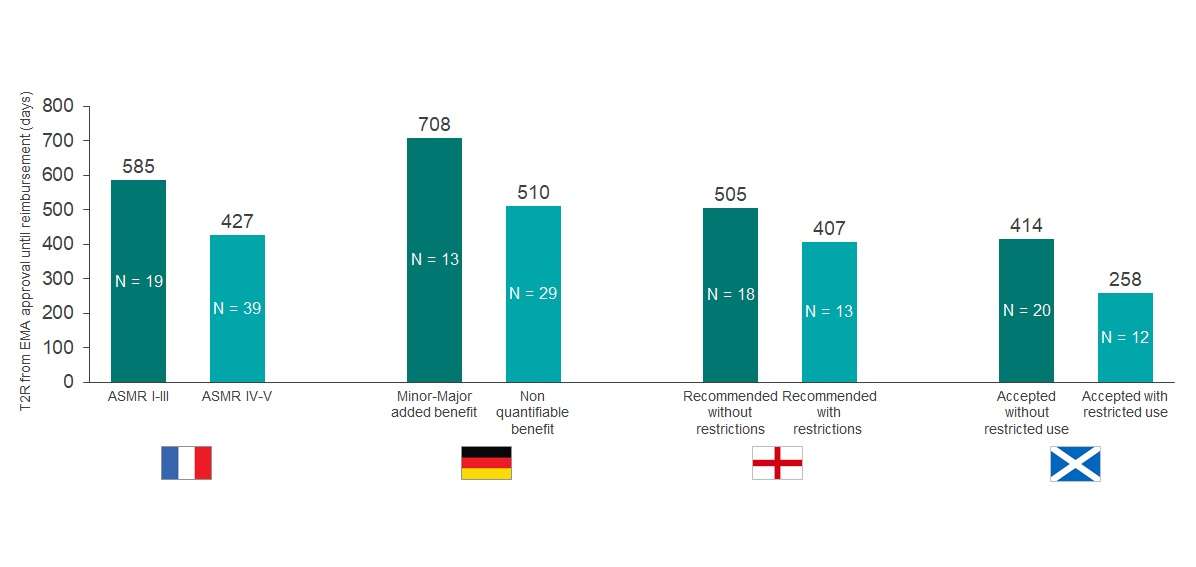
Graph 2: Comparison of the time to reimbursement (days) for EMA orphan drugs accepted from 2013- 2019. Orphan drugs had been reimbursed in no less than one of many chosen markets (N = 70). N inside every bar equals the variety of drugs with every consequence reviewed by the respective HTA physique. Source: CRA Analysis
In England, two key mechanisms had been usually used to realize approval: label restrictions or a affected person entry scheme (PAS).
Over one third (37%) of orphan drugs appraised by NICE solely achieved approval in a positioning or inhabitants that was restricted versus the complete regulatory accepted label. Companies that accepted such restrictions noticed sooner approval time in comparison with no drugs with restrictions (407 versus 505 days).
Meanwhile, though introducing a PAS improved the possibility of approval, the evaluation means that it truly delays the general appraisal time (523 versus 311 days).
Scotland had the very best charge of non-approval for orphan drugs. Thirty-three % of drugs reviewed weren’t accepted, regardless of particular modifiers in place for uncommon illness merchandise, together with the incorporation of the affected person voice by the nation’s Patient and Clinician Engagement (PACE) conferences – which had been included in 74% of orphan drug submissions between 2013-2019.
Improving HTA outcomes
The authors conclude that whereas the assorted concessions and modifiers launched by completely different governments have a constructive impression on minimising rejections and accelerating approval instances, there are nonetheless challenges in capturing the complete worth of orphan drugs throughout the HTA course of.
“Achieving more favourable outcome ratings, avoiding restrictions, or addressing uncertainty with a PAS all lead to prolonged appraisal times,” the authors say. “Manufacturers are therefore still required to consider carefully their HTA launch strategy and complement this with additional evidence generation and engagement from a wider stakeholder group.”
The authors define a number of approaches firms can take to enhance the probabilities of success in orphan drug approvals and overcome the problem of getting restricted information and proof obtainable.
One method is to agree strategies for ongoing actual world information assortment post-launch with HTA our bodies.
They add that “creative” options to actual world proof assortment may assist, comparable to growing apps for sufferers and HCPs.
Meanwhile, additionally it is essential to attempt for wider engagement with the uncommon illness group and different stakeholders.
Listening to views from sufferers and HCPs will help with processes like Scotland’s PACE conferences – however extra oblique types of stakeholder engagement can also enhance HTA outcomes, because the value-added companies offered to those stakeholders could be leveraged throughout negotiations.
“For example, Galafold, an enzyme replacement therapy for Fabry’s disease, is primarily differentiated from existing treatments by providing a reduction in administrative burden,” the authors say. “Despite this, Galafold was able to achieve an ASMR IV in France, recommendation by NICE, and was accepted for restricted use in Scotland.”
They notice that the notion of Galafold’s worth could have been improved by the extra value-added companies the producer, Amicus Therapeutics, supplied to a wider stakeholder group
For instance, Amicus reimbursed amenability exams for sufferers with unknown mutations that may very well be referenced in opposition to Galafold’s amenability desk by way of a doctor help web site. This service was accepted within the NICE analysis as one thing which averted further useful resource implications for the NHS.













